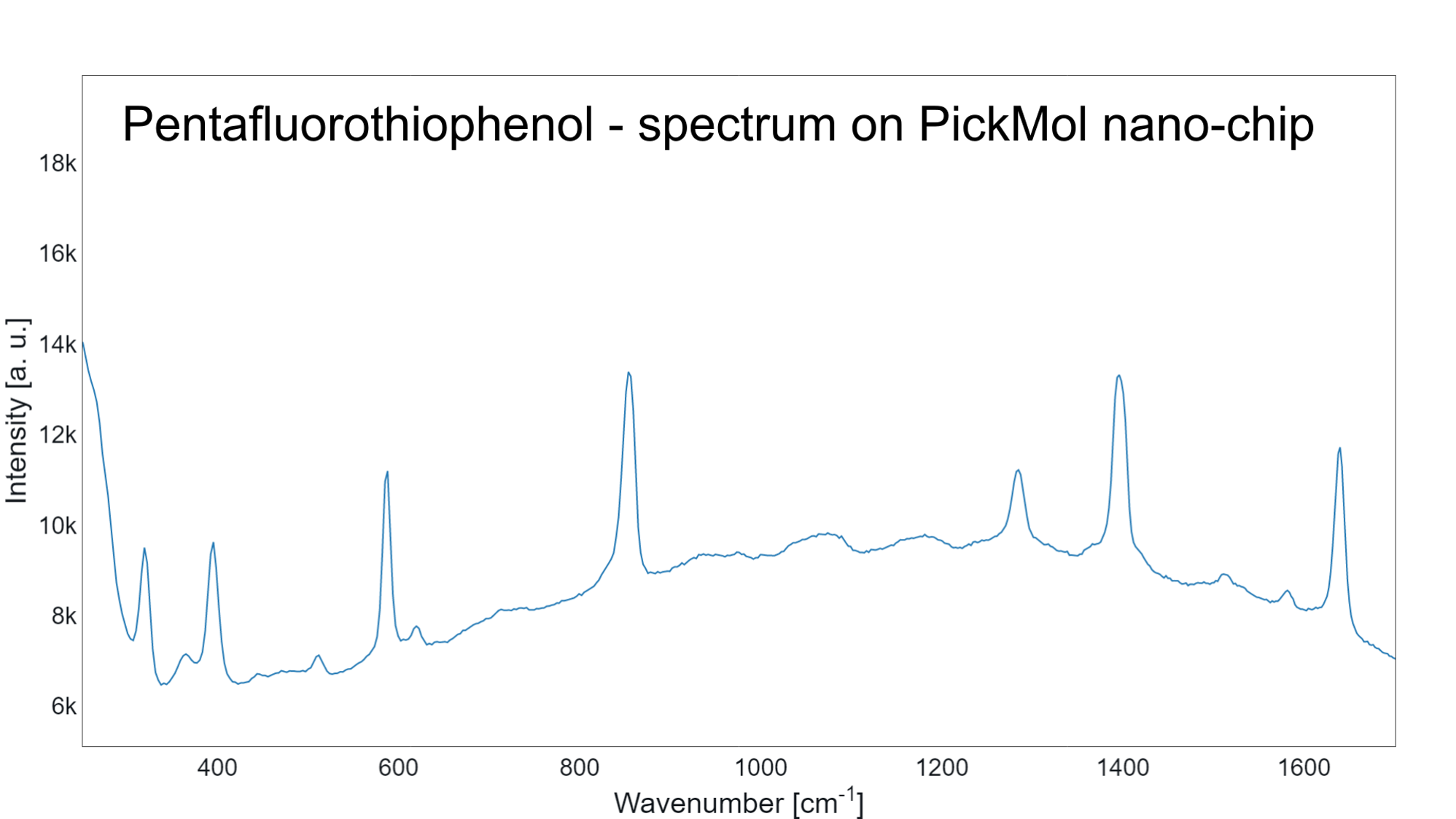
Molecular Database
2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorothiophenol
MW: 200.13 g/mol
CAS Number: 771-62-0
Use and production
Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a human-made family of compounds. PFAS generally contain multiple F–C bonds, which lead to their unique properties, such as simultaneous hydrophobicity and oleophobicity, that is not seen in other compounds. Consequently, PFAS have become widely used in items such as clothing, upholstery, carpeting, painted surfaces, food containers, cookware and firefighting foams. Unfortunately, the F–C bond is among the most stable covalent bonds known in chemistry, and is highly resistant to degradation. Because of their widespread use and high persistence, they are detected all over the world – from in humans to the deep sea. Thus, their monitoring is urgently needed.
Toxicity
Current scientific research suggests that exposure to high levels of certain PFAS may lead to adverse health outcomes. However, research is still ongoing to determine how different levels of exposure to different PFAS can lead to a variety of health effects. Research is also underway to better understand the health effects associated with low levels of exposure to PFAS over long periods of time, especially in children.