Molecular Database
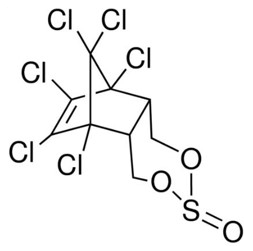
α-Endosulfan
MW = 406.93 g/mol
CAS Number: 959-98-8
Use and production
According to the risk management evaluation on endosulfan, adopted by the POPRC, endosulfan is an insecticide that has been used since the 1950s to control crop pests, tsetse flies and ectoparasites of cattle and as a wood preservative. As a broad-spectrum insecticide, endosulfan is currently used to control a wide range of pests on a variety of crops including coffee, cotton, rice, sorghum and soy.
A total of between 18,000 and 20,000 tons of endosulfan are produced annually in Brazil, China, India, Israel and South Korea. Colombia, the United States of America and several countries in Europe that used to produce endosulfan have stopped its production. An additional 21 countries report using endosulfan. The use of endosulfan is banned or will be phased out in 60 countries that, together, account for 45 percent of current global use.
Toxicity and POPs characteristics of endosulfan
Endosulfan is listed under Annex A in the Stockholm convention with specific exemptions.
According to the risk profile on endosulfan, adopted by the POPRC, endosulfan is persistent in the atmosphere, sediments and water. Endosulfan bioaccumulates and has the potential for long-range transport. It has been detected in air, sediments, water and in living organisms in remote areas, such as the Arctic, that are distant from areas of intensive use.
Endosulfan is toxic to humans and has been shown to have adverse effects on a wide range of aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Exposure to endosulfan has been linked to congenital physical disorders, mental retardations and deaths in farm workers and villagers in developing countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America.