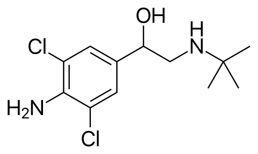
Molecular Database
Clenbuterol
MW: 277.19 g/mol
CAS Number: 37148-27-9
Use and production
Clenbuterol is a chemical called a beta-2-adrenergic agonist. It has approval in the United States for use in horses with breathing difficulty.
Clenbuterol is both a decongestant and a bronchodilator. A decongestant works by narrowing and constricting blood vessels to reduce congestion. Conversely, a bronchodilator helps relax the muscles around the airway, which in turn opens it up.
In some European and Latin American countries, clenbuterol has approval for human use as an asthma drug. However, in the U.S, it is banned to use it for this purpose.
The drug is also controversial because of its use in bodybuilding and weight-loss programs.
Toxicity
Clenbuterol is well-known to cause symptoms such as rapid heart rate (tachycardia), palpitations, tremors, anxiety, lowered blood potassium (hypokalemia), and elevated blood sugar (hyperglycemia). Adverse effects happen more often with the large doses used for performance enhancement and weight loss. Because the drug has a long half-life in the body, toxic symptoms can last from 1 to 8 days. In one published report, over 80% of people who developed toxic effects required care in a hospital. The medical literature contains numerous reports of patients with symptoms ranging from agitation and rapid heart rate all the way to heart attack and cardiac arrest.
Clenbuterol has been listed by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and the International Olympic Committee (IOC) as a performance-enhancing drug that is banned in competitive sports.